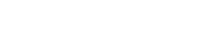Integrating PI, P&ID, and Business System Data into a Unified Knowledge Graph Using DeepIQ
Abstract
Industrial operations generate large volumes of data from historians, engineering systems, and business applications. Yet these datasets are typically trapped in separate silos, limiting analytics, optimization, and digital-transformation efforts.
- PI AF hierarchy and time series data (from OSIsoft PI),
- P&ID-derived connectivity and topology,
The result is a semantically rich, queryable model that links operational data, engineering context, and business intelligence into a single digital twin.
Business systems such as SAP and Maximo contain rich operational, maintenance, and transactional data. DeepIQ enables users to ingest this information and seamlessly integrate it into the unified knowledge graph. Since this topic is covered extensively in other DeepIQ whitepapers (1 and 2), it is not discussed in detail here.
Overview of DeepIQ Integration Architecture
DeepIQ provides a unified low-code/no-code environment for industrial data integration and knowledge graph creation.
Using its modular workflows, users can ingest, transform, and harmonize data from multiple sources into a connected data model.
Key Components
DeepIQ’s integration architecture brings together industrial, engineering, and business data through a set of modular, interoperable capabilities. These components work in concert to ingest, enrich, align, and connect information from diverse sources into a unified, semantically consistent knowledge graph.
- DeepIQ P&ID Extraction Workflow: Utilizes proprietary Generative AI models to extract entities and relationships from engineering drawings with industry-leading accuracy.
- DeepIQ PI Ingestion Workflow: Connects to PI AF to extract both hierarchical structures and live time-series data.
- DeepIQ Transformation Workflows: Standardize, harmonize, and align entities from PI and P&ID sources into a unified schema.
- DeepIQ Knowledge Graph Builder: Links all extracted and transformed information into a common data model, enabling exploration, analysis, and visualization of the connected knowledge graph.
As depicted in Figure 1, DeepIQ’s architecture enables seamless integration of disparate industrial data sources into a unified model.
We now illustrate how this process can be executed in DeepIQ in a few simple steps.
Step 1: Extracting P&ID Network Topology
The DeepIQ P&ID Extraction Workflow processes engineering drawings to extract:
Equipment and instrument symbols (nodes),
Connectivity paths (edges), and
Relationship semantics (process flow, signal, or mechanical links).
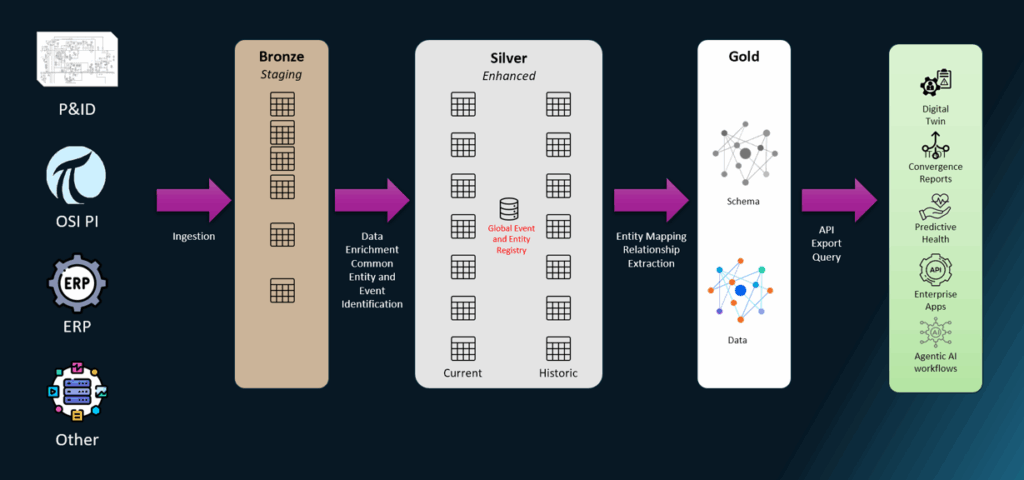
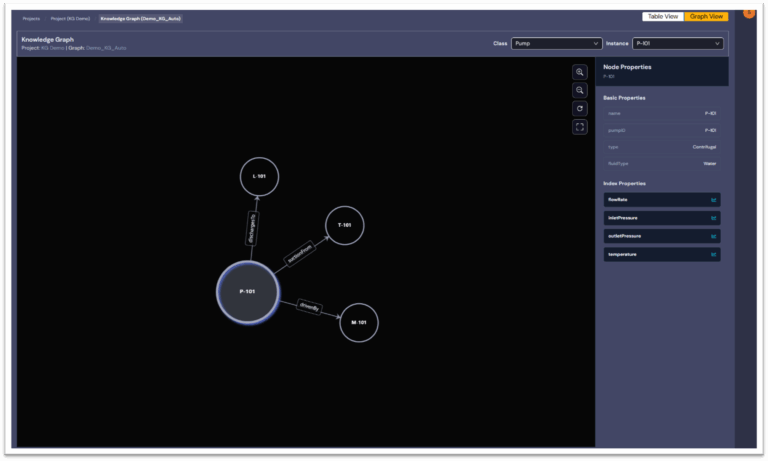
. A sample (simplified) view of the extracted network topology is shown in Figure 3

This creates a semantic network model describing how assets interact rather than just what they are.
Step 2: Extracting the PI AF Hierarchy
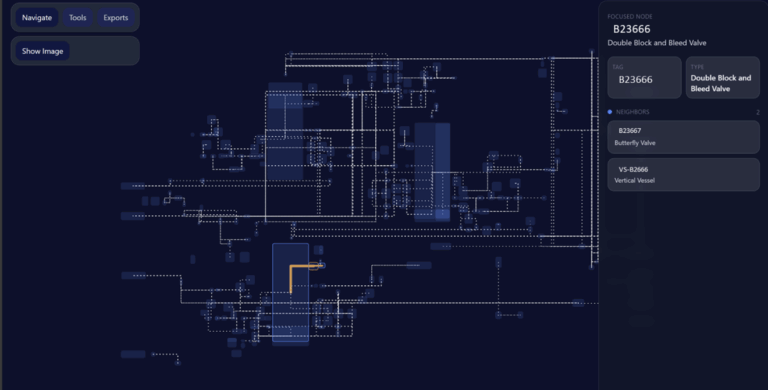
The DeepIQ PI Ingestion Workflow connects to the OSIsoft PI AF server and extracts:
- The asset hierarchy (e.g., motors, pumps, tanks, valves, controllers, transmitters),
- The element templates and attribute definitions, and
- The associated PI tag mappings for each property.
DeepIQ Data Integrator provides a unified and secure interface for accessing operational data sources within air-gapped environments. To comply with industrial network security constraints, Data Integrator does not require any inbound connectivity into protected OT zones. Instead, it leverages a connector agent deployed inside the secured network, which initiates outbound, firewall-approved requests to local data sources.
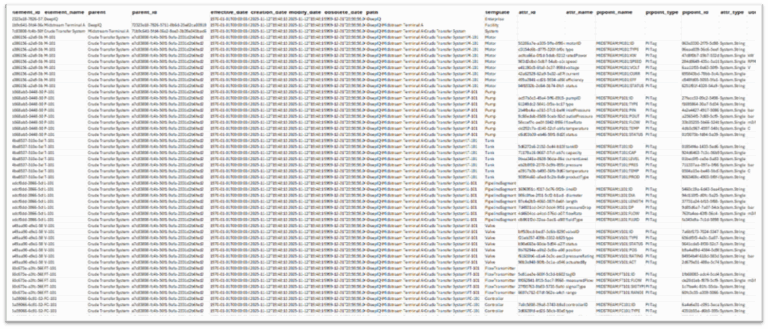
The AF hierarchy is monitored for changes and ingested as a structured JSON as shown below.
Step 3: Defining the Knowledge Graph Schema
DeepIQ’s knowledge graph schema acts as the unifying model connecting PI, P&ID, and business data.
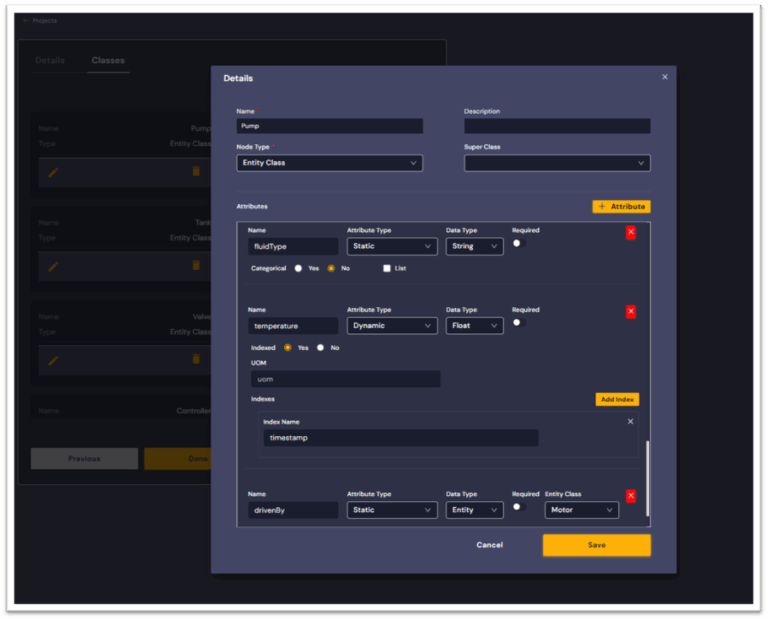
While the above UI shows a manual way of creating the knowledge graph schema, DeepIQ provides extensive support for generating these schemas automatically using existing data sources such as OPC UA hierarchies, AF template classes or external OWL ontologies.
In our simple example, we create definition of classes, attributes, and relationships, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Core Equipment Classes, Properties, and Relationships in the DeepIQ Knowledge Graph Schema
| Class | Example Properties | Example Relationships |
|---|---|---|
| Pump | flowRate, inletPressure, outletPressure | drivenBy(Motor), suctionFrom(Tank) |
| Motor | speed, voltage, current | drives(Pump) |
| Tank | level, pressure | feeds(Pump) |
| Valve | position, type | controlledBy(Controller) |
| Controller | setPoint, outputSignal | controls(Valve) |
| FlowTransmitter | measuredFlow | monitorsFlowIn(Pipeline) |
Step 4: Creating Knowledge Relationships and Instances
Now, that the schema is available, we move the next step of populating the instances and relationships in the schema.
The DeepIQ AF Transformation Workflow converts the extracted AF JSON into actual entity instances in the knowledge graph.
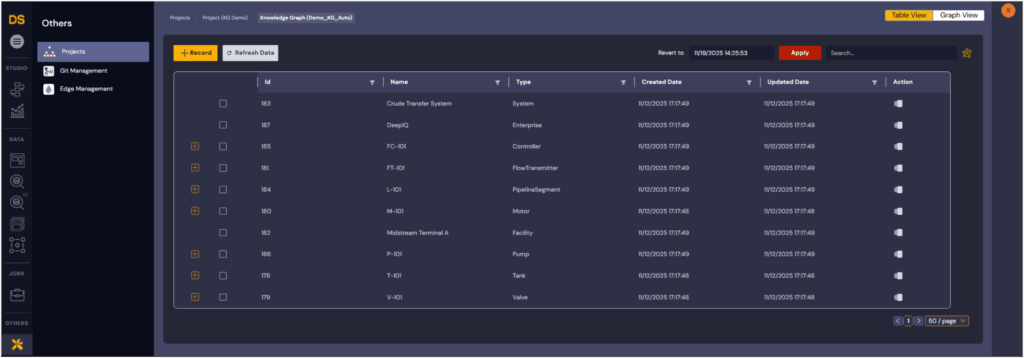
In our simple example in Table 2, the following instances are created.
Table 2: Sample Asset Instances and Equipment Types Created in the DeepIQ Knowledge Graph
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| M-101 | Motor |
| P-101 | Pump |
| T-101 | Tank |
| L-101 | PipelineSegment |
| V-101 | Valve |
| FT-101 | FlowTransmitter |
| FC-101 | Controller |
Each instance inherits its attributes from the AF data (e.g., ratedPower, inletPressure, flowRate) and is automatically mapped to its PI tag references.
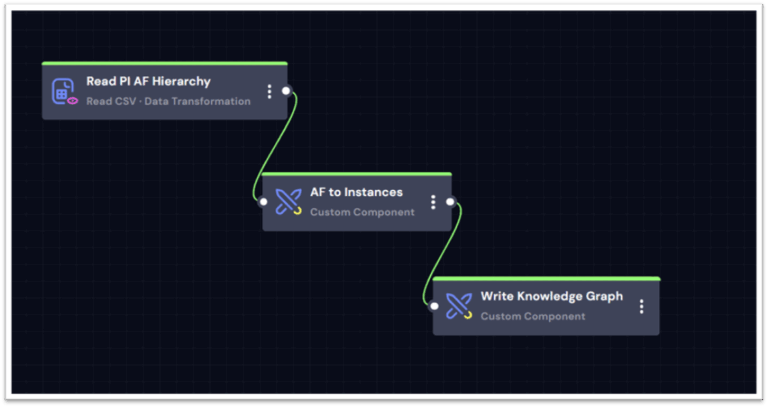
The DeepIQ P&ID Transformation Workflow establishes relationships between instances based on the extracted connectivity model as shown in Table 3:
Table 3: Asset Relationships and Their Operational Meanings in the DeepIQ Knowledge Graph
| Relationship | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Pump P-101: drivenBy→ Motor M-101 | Mechanical link |
| Pump P-101: suctionFrom→ Tank T-101 | Fluid source |
| Pump P-101: dischargesTo→ PipelineSegment L-101 | Fluid discharge |
| L-101: hasValve→ Valve V-101 | Flow control |
| FlowTransmitter FT-101: monitorsFlowIn→ L-101 | Measurement |
| Controller FC-101: receivesSignalFrom→ FT-101 | Signal input |
| Controller FC-101: controls→ V-101 | Control output |
This step links the static equipment structure from AF with functional logic from P&ID.
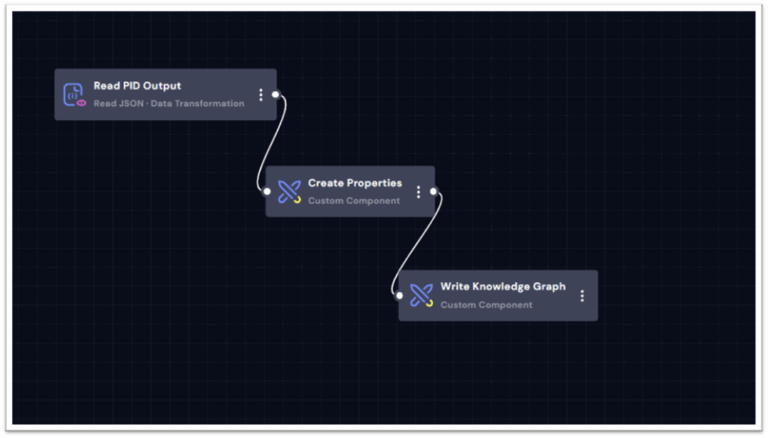
Step 6: Ingesting and Linking PI Time Series Data
The DeepIQ PI Time Series Ingestion Workflow continuously ingests live and historical process data from PI Data Archive and associates it with the relevant entity properties in the graph.
The data enrichment work also enriches timeseries data using advanced statistical algorithms including interpolation, imputation and noise removal.
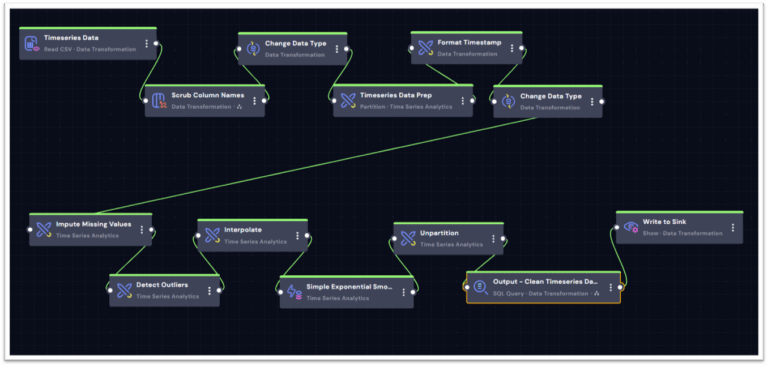
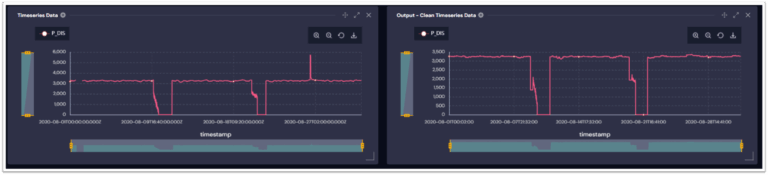
This makes time series trends directly available within the knowledge graph context, enabling queries like:
“Show flow rate vs motor current for Pump P-101 during the last 24 hours.”
Step 7: Unified View in the Knowledge Graph
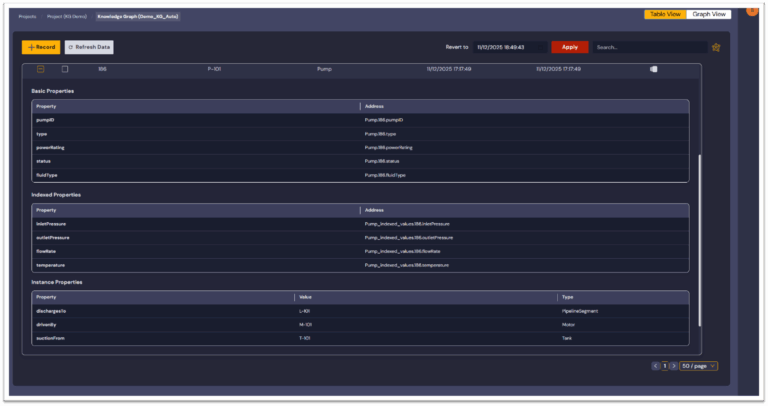
Once both AF and P&ID transformations are complete, we have implemented a connected knowledge graph where:
- Equipment, instruments, and pipelines are nodes,
- P&ID relationships are edges, and
- PI attributes and time series are attached as properties.
This provides a single queryable layer that combines:
- Operational context (from PI),
- Physical connectivity (from P&ID),
- And optional business metadata (from ERP, CMMS, or inventory systems).
Benefits of This Integrated Approach
The integration of PI, P&ID, and business system data using DeepIQ’s knowledge graph platform delivers a range of significant benefits for industrial operations. By unifying engineering, operational, and business information into a single, connected model, organizations can unlock new capabilities in analytics, streamline data access, and scale insights across assets and facilities.
Table 4 summarizes the key capabilities enabled by this approach and the value they provide.
Table 4: Key Capabilities and Value Enabled by DeepIQ’s Integrated Knowledge Graph Approach
| Capability | Enabled By | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unified digital twin | DeepIQ Knowledge Graph | Combines engineering, operational, and business data |
| Contextual analytics | PI + P&ID integration | Enables root-cause and performance correlation |
| Simplified data access | DeepIQ transformations | Single semantic layer for analytics tools |
| Scalability | DeepIQ orchestration | Works across assets, units, or entire facilities |
Conclusion
This example illustrates how DeepIQ simplifies the creation of an industrial knowledge graph that integrates engineering, operational, and business data sources.
By combining PI AF hierarchies, P&ID topologies, and time series data, DeepIQ enables:
- Holistic visibility into process behavior,
- Contextualized analytics and machine learning, and
- A foundation for autonomous optimization and predictive maintenance.
To learn more about DeepIQ, explore our Customer success stories or engage with us through a focused pilot to experience the platform’s capabilities firsthand. Contact us at info@deepiq.com to begin your transformation journey.